Hydrophobicity peptides are:
Containing >50% hydrophobic amino acids
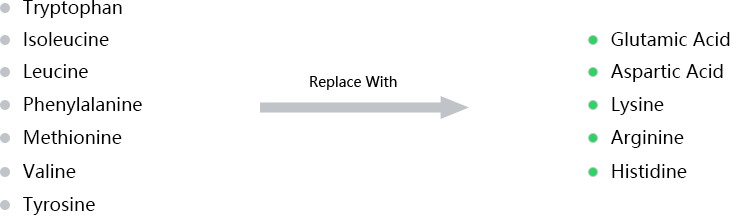
Solution: Avoid hydrophobicity by replacing non-essential hydrophobic amino acids with charged or polar residues.
Design basics III: length
You can design peptides with any length, but from the positon of peptide synthesis, the difficluty of synthesis will increase as the growth of the peptide length. So we suggest you design the peptide with the length between 15-20 animo acids residues, peptides with < 30 amino acids residues can be synthesized at most conditions, but the success rate to synthesize the peptide with >40 amino acids will be greatly reduced.
Design basics IV:purity selection
HongTide proposes a range of different purity levels to help you make the right choice for your application. Crude peptides are not recommended for biological assays. Crude peptides may contain large amounts of non-peptide impurities such as residual solvents, scavengers from cleavage, TFA and other truncated peptides. TFA cannot be totally removed. Peptides with purity >70% are always used for generating or testing antibodis. Peptides with purity level >85% are usually used in enzymology or biological activity studies. Peptides with purity >95% are excellent for quantitative analysis. We also provide purity peptides with purity >98% in large quantities with commercial applications for our industrial customers. HongTide recommends the following levels of peptide purity for various projects:















 Contact us by We-chat.
Contact us by We-chat.